
Italy
Dashboard Indicators
-
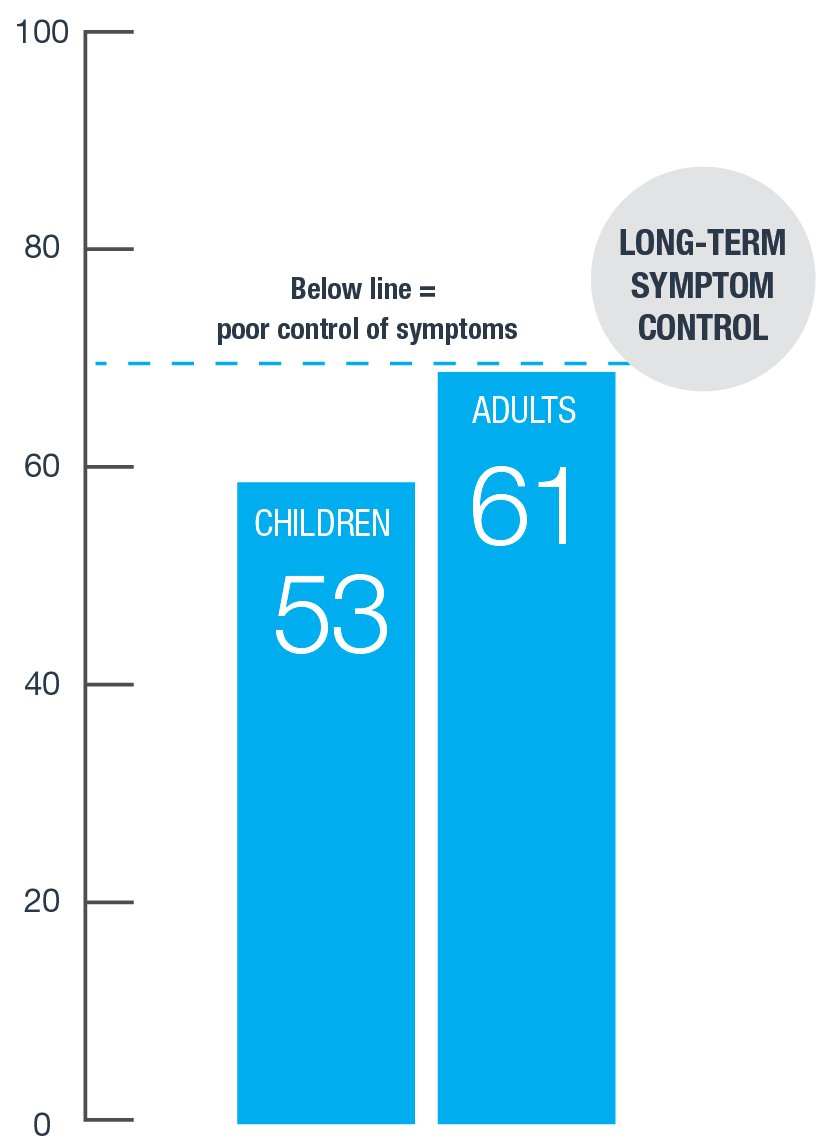
Long-term Control of Eczema Symptoms
Scores are based on responses to the AD Control Tool: https://www.adcontroltool.com/adct-how-to-use/adct-in-clinical-practice
Data source: GPIIEC global survey of 3,253 patients and caregivers, 2022.
-
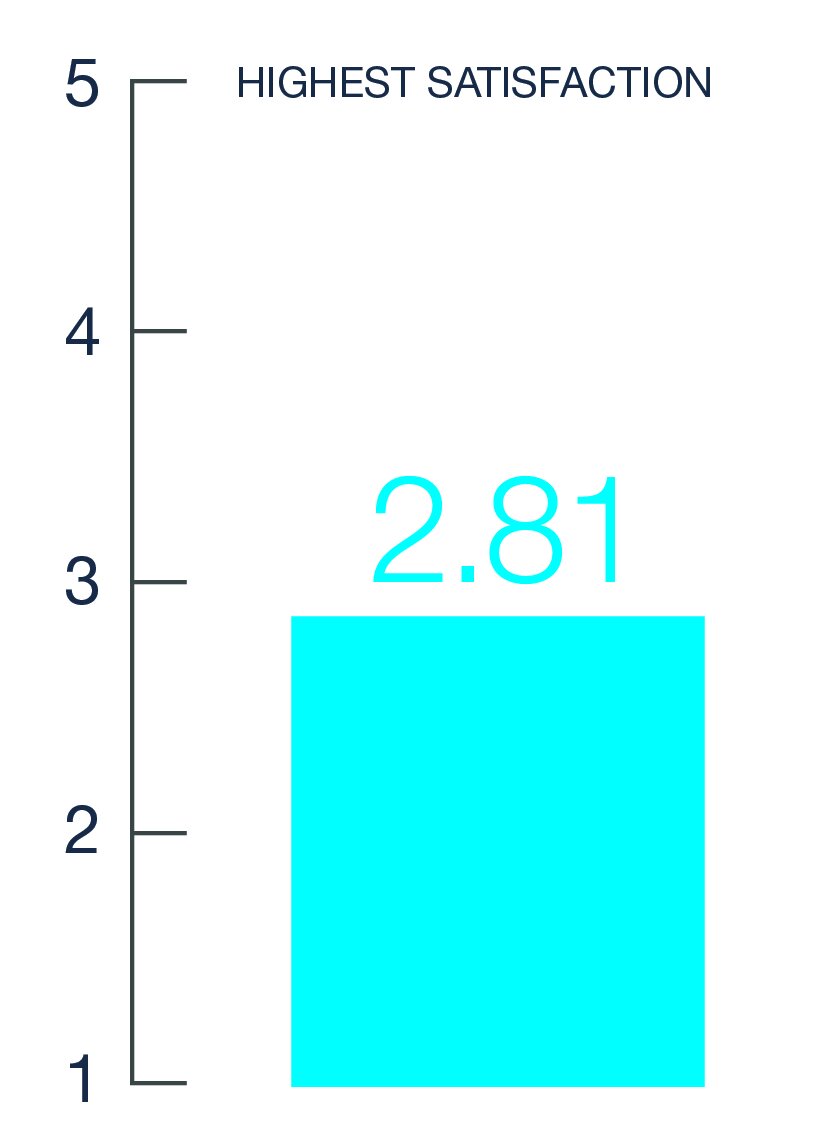
Satisfaction with Eczema Treatments
Self reported satisfaction with current treatments (caregivers and adults).
Data source: GPIIEC global survey of 3,253 patients and caregivers, 2022.
-

Life Span Trade-Off (Health Utility)
Percent of remaining life span adult patients would trade off in order to be restored to perfect health. (Derived from EQ5D Utility Scores).
Data source: GPIIEC global survey of 3,253 patients and caregivers, 2022.
-
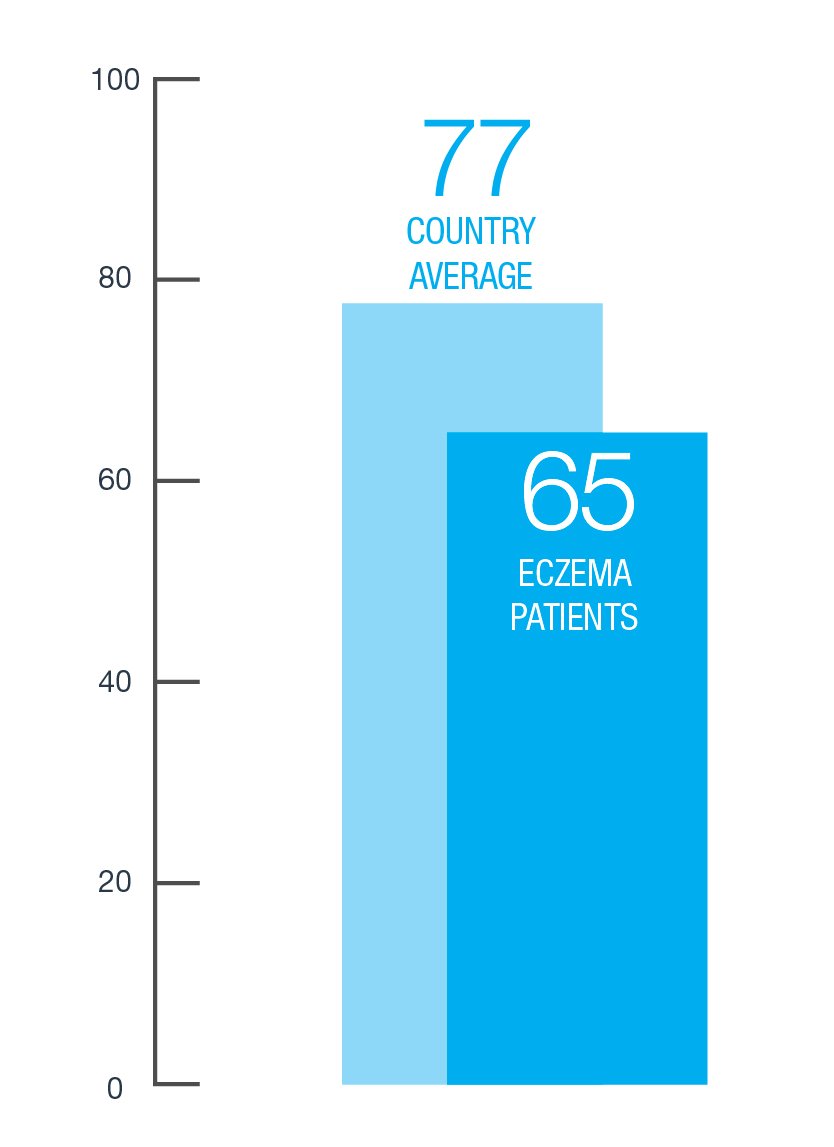
Eczema Patients Self Reported Health to Compared to Country Average
Self-rated quality of life score for the average person compared to the self-rated quality of life score for adults with eczema.
Data source: GPIIEC global survey of 3,253 patients and caregivers, 2022.
-
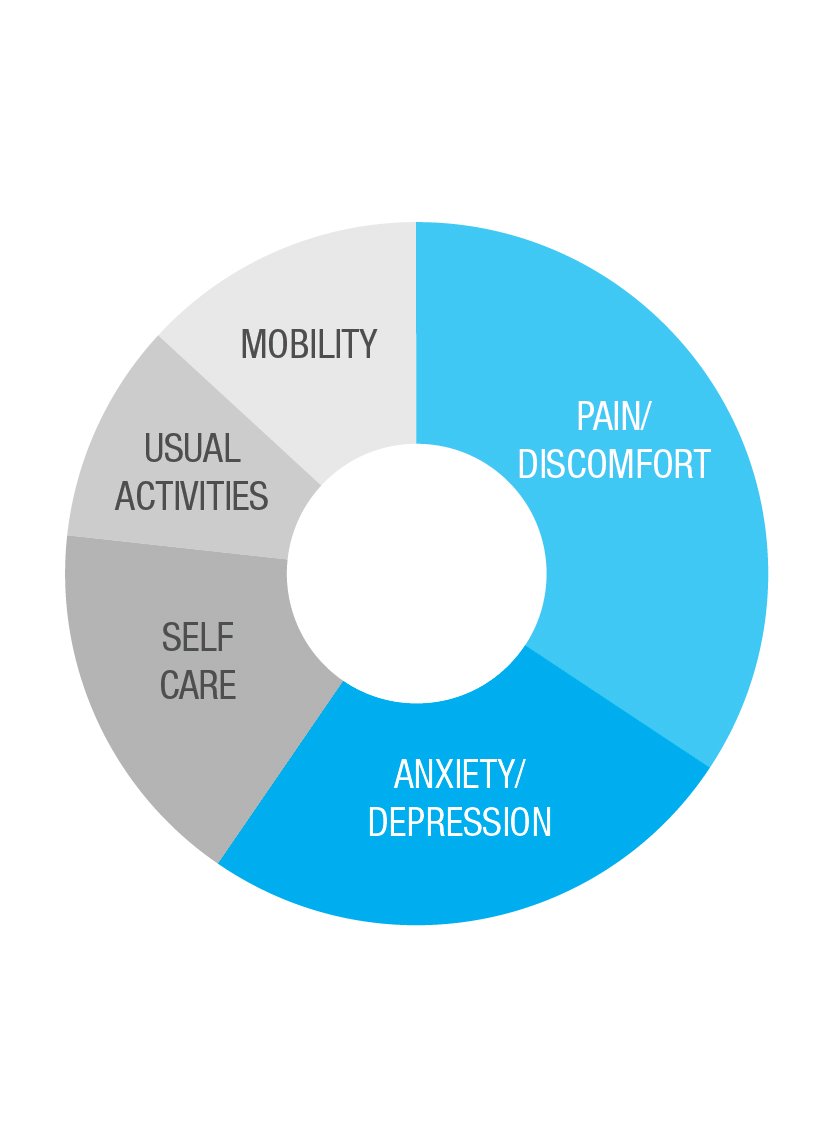
Dimensions of Health – Relative Impact (Adults)
Data source: GPIIEC global survey of 3,253 patients and caregivers, 2022.
-

Financial Burden – Impacts
Percent of respondents (adults and caregivers) who reported using savings, borrowing money and/or reducing spending due to eczema. Higher = More Financial Impact
Data source: GPIIEC global survey of 3,253 patients and caregivers, 2022.
-

Shared Decision Making
The percentage of respondents who indicated that the healthcare provider whom they see for eczema asked about their priorities for their eczema care at the most recent visit.
Data source: GPIIEC global survey of 3,253 patients and caregivers, 2022.
-

Eczema Education and Training
Respondents who said a health care provider had ever suggested they attend an eczema training program that happens after the office visit.
Data source: GPIIEC global survey of 3,253 patients and caregivers, 2022.
-

Access to Dermatologists
Italy ranked 2nd out of the 10 countries in access to dermatologists.
Source: “Physicians by Medical Specialty .” Eurostat , 2016, appsso.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/nui/show.do?dataset=hlth_rs_spec&lang=en.
-

Evidence-Based Guidelines
Italy’s guidelines met most criteria, however they did not include patient or caregiver input.
Scoring criteria for the guideline measure >
Source: Damiani, Giovanni, et al. “Italian Guidelines for Therapy of Atopic Dermatitis—Adapted from Consensus‐based European Guidelines for Treatment of Atopic Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis).” Dermatologic Therapy, vol. 32, no. 6, Wiley, Nov. 2019.
Literature Review Key Findings
The prevalence and persistence data in Italy are notable for the high rate at which childhood AD lasted into adulthood. The data on comorbidities are sparse, so future population-based studies are warranted.
The Italian literature paints a picture of caregiver burden. Of the many dimensions of the psychosocial burden, sleep disturbances were common in both children with AD and their caregivers. Caregivers’ well-being was also affected by fatigue/irritability and the costs associated with disease management. One study found that a child’s severe AD had a greater impact on the family’s quality of life than on the child’s own quality of life; the inadequacy of AD education seemed to contribute to the caregiver burden.As in Germany and the UK, an educational program for Italian parents of children with AD was successful at improving the parents’ psychological well-being.
Learn more about the findings gathered from the Italy literature review.
